A multilayer fitting to combat the risk of legionella
The most recent data from the National Institute of Health confirm an increase in legionella cases in Italy. In 2022, 3111 cases of legionellosis were recorded, an increase of 14% over the previous year.
What is legionella and how it is transmitted
Legionella, or legionnaire’s disease, is a lung infection that occurs after an incubation period ranging from 2 to 10 days. Symptoms can be severe and include fever, cough, chest pain, dyspnea, and cyanosis, with equally significant complications.
This disease is caused by a group of bacteria that feed on organic material in the environment and are sensitive to the presence of Iron, an element that stimulates their metabolism. Legionella disease is transmitted by air, by inhaling aerosolized water particles (in form of vapour), as occurs while showering or in air-conditioned enviroments.
Plumbing systems and legionella
Considering the preferred habitat of Legionella bacteria, the structures most at risk of contamination can be identified as follows:
- Sanitary plumbing, such as piping, sanitary storage tanks, faucets, valves and mixers, shower heads.
- Cooling towers, including evaporative condensers and closed or open circuit towers.
- Heated pools and baths, such as hot tubs and spa pools.
- Air conditioning systems, including evaporative pack humidifiers, foggers, filters, and silencers.
Places that link the different contamination factors are those most at risk of contamination and spread of the bacterium, for examples hospitals with intensive care, transplantation, and neonatology departments, followed by medium risk for other hospital departments, retirement homes, buildings used for sports activities, hotels, schools with showers, and homes with centralized hot water systems. At low risk, on the other hand, are homes and offices with instantaneous water distribution, restaurants, and commercial structures.
Aquatechnik solutions against legionella
The implementation of procedures and technical choices that can reduce the risk of legionellosis is essential at any level, from the design stage to the management and maintenance stage of structures.
At the design stage, it is essential to consider how the temperature factor is a relevant element in preventing the proliferation of bacterial colonies. The ideal habitat for bacterial proliferation is between 20°C and 40°C, while from 45°C there is inactivation of the bacteria in 5-6 hours and in a few minutes at temperatures above 60°C.
The prevention of legionella development starts with a wide design concept that excludes the use of pipes with blind ends, without circulation and with risk of stagnation, in favour of materials with low surface roughness and high temperature resistant, supported by a jointing system that avoids the formation of deposits.
Aquatechnik’s systems have very low internal roughness compared to steel: 0.007 mm for PP-RCT WOR fiber-reinforced pipes and PE-X/AI/P-EX multilayer pipes, compared to 0.03 mm for steel. In addition, Multi-calor and Fusio-technik pipes, particularly in the fiber-reinforced Faser version, are perfect thanks to their chemical and high temperature resistance for optimal results during thermal shock and chemical disinfection of facilities.

Full-bored joints Safety prevent the formation of deposits
Full-bored fittings: Threaded tee female angle 90°
Safety-plus fittings are a guarantee of total flow, as to avoid the formation of deposits, compared with other traditional systems, where the joining method causes a narrowing of the section.
For this purpose, we have designed a special fitting that, once installed, can help prevent health emergencies. In response to the growing domestic and international market demands for the control of legionella bacteria in plumbing systems, the threaded tee female angle 90° is an effective and durable solution with all the installation and performance advantages of Aquatechnik’s Safety range of multilayer fittings.
It is a 90° PPS fitting with ½ “brass alloy female thread for 16 mm diameter pipes, which can be used in series and in ring circuit applications and ensures a high flow passage to to the final draw off circuit, minimising water stagnation at any point in the system. The threaded tee also facilitates continuous water flow, reducing the risk of stagnation and ensuring high levels of hygiene.
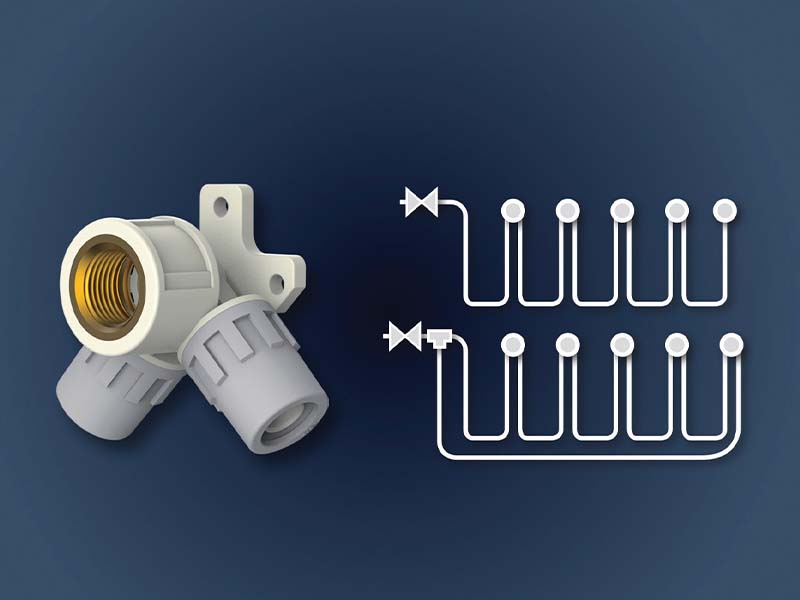
Threaded tee female angle 90° prevents the risk of water stagnation
Other advantages include the possibility of creating a greater number of water distribution points for better savings in terms of money and processing waste. Like all parts of the Safety range, it is designed for the distribution of hot and cold potable water.